- About
- Academics
-
Undergraduate Programs
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Architecture and Architectural Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy Resources Engineering
- Nuclear Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
-
Graduate Programs
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Architecture and Architectural Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy Systems Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Interdisciplinary Program in Technology, Management, Economics and Policy
- Interdisciplinary Program in Urban Design
- Interdisciplinary Program in Bioengineering
- Interdisciplinary Program in Artificial Intelligence
- Interdisciplinary Program in Intelligent Space and Aerospace Systems
- Chemical Convergence for Energy and Environment Major
- Multiscale Mechanics Design Major
- Hybrid Materials Major
- Double Major Program
- Open Programs
-
Undergraduate Programs
- Research
- Campus Life
- Communication
- Prospective Students
- International Office
SNU Professor Ki Tae Nam’s research team developed nanoparticle catalyst which reveals principles of photosynthesis and demonstrated water oxidation reaction mechanism for the first time
-
Uploaded by
관리자
-
Upload Date
2017.06.09
-
Views
762
SNU Professor Ki Tae Nam’s research team developed nanoparticle catalyst which reveals principles of photosynthesis and demonstrated water oxidation reaction mechanism for the first time
- Innovative nanoparticle catalytic material based on eco-friendly and cheap manganese
- Provide technology thresholds in the area of electrochemical catalyst of lithium-air battery and fuel cell

▲SNU Department of Materials Science and Engineering Professor Ki Tae Nam research team; (Left) Professor Ki Tae Nam, Doctor Kyoungsuk Jin and Researcher Hongmin Seo
- Provide technology thresholds in the area of electrochemical catalyst of lithium-air battery and fuel cell

▲SNU Department of Materials Science and Engineering Professor Ki Tae Nam research team; (Left) Professor Ki Tae Nam, Doctor Kyoungsuk Jin and Researcher Hongmin Seo
The research which incorporated principles of photosynthesis in artificial catalyst was conducted by domestic researchers for the first time.
SNU College of Engineering (Dean Lee Kun-woo) stated on 13th that Professor Ki Tae Nam’s research team (Doctor Kyoungsuk Jin and Researcher Hongmin Seo) developed new manganese based nanoparticle catalyst which reveals core reaction mechanism.
This research is expected to be applied in various areas of hydrogen production and fuel cell. In addition, this research is acclaimed as a real progress in biocatalyst reproduction technology by demonstrating efficiency and reaction mechanism of water oxidation in nature.
The research team said, “There is a water oxidation complex (WOC) of organic and inorganic cluster in Photosystem II. The turnover frequency of this calcium and manganese WOC in plants and bacteria is much higher than metal catalyst.”, and they said “We have tried to mimic the properties of biocatalyst. Without having clear results due to the low stability, we aimed to solve this problem.”
The research team noticed unique electrochemical properties of nano manganese oxide surface and adopted this into water oxidation mechanism. As the result, electrochemical reaction of water oxidation showed high advanced property.
Also, through collaborative research with Doctor Ryuhei Nakamura’s research team of Japan RIKEN, they demonstrated water oxidation mechanism of the manganese catalyst for the first time. They revealed that there is completely different reaction mechanism from previous manganese catalyst, and proved that this is similar to core principles of the calcium-manganese cluster.
The manganese oxide nanoparticle developed by the research team is 50 times more efficient than previous ones. Especially, the catalyst has price competitiveness since it only composed of cheap manganese (2$/kg) not metal. These are the reason why it can be used as candidate material which can replace currently commercialized Platinum.
Professor Nam said, “This newly developed nano catalyst is innovative that it is based on manganese which demonstrates core principle of photosynthesis and which is both eco-friendly and cheap,” and he said “By clarifying unique properties of the nanoparticle, it will provide technological threshold in various areas of electrochemical catalyst such as lithium-air battery and fuel cell.
Meanwhile Professor Ki Tae Nam’s research team was composed of Professor Ryuhei Nakamura for Japan RIKEN, Doctor Sun Hee Kim from Korea Basic Science Institute, and Doctor Min Gyu Kim from Pohang Accelerator Laboratory. The research results were published online in Journal of the American Chemical Society which is the world’s most renowned journal in chemistry.
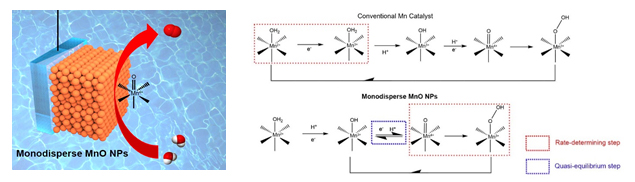
▲Figure 1: Diagram for water oxidation of manganese oxide nanoparticle (left), reaction mechanism of general manganese based water oxidation catalyst and that of newly developed manganese oxide by the researchers (right)
-
NextSNU Ki Yun Yu research team developed location selection model for AED accessibility improvement