- About
- Academics
-
Undergraduate Programs
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Architecture and Architectural Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy Resources Engineering
- Nuclear Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
-
Graduate Programs
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Architecture and Architectural Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy Systems Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Interdisciplinary Program in Technology, Management, Economics and Policy
- Interdisciplinary Program in Urban Design
- Interdisciplinary Program in Bioengineering
- Interdisciplinary Program in Artificial Intelligence
- Interdisciplinary Program in Intelligent Space and Aerospace Systems
- Chemical Convergence for Energy and Environment Major
- Multiscale Mechanics Design Major
- Hybrid Materials Major
- Double Major Program
- Open Programs
-
Undergraduate Programs
- Research
- Campus Life
- Communication
- Prospective Students
- International Office
News
SNU Electrical and Computer Engineering Team Develops AI Training Method to Enhance Large Language Model Alignment, Earns ICML 2025 “Spotlight” Selection
-
Uploaded by
대외협력실
-
Upload Date
2025.08.04
-
Views
1,662
SNU Electrical and Computer Engineering Team Develops AI Training Method to Enhance Large Language Model Alignment, Earns ICML 2025 “Spotlight” Selection
- Paper ranks in top 2.6% at the world’s premier AI conference, highlighting Korea’s AI capabilities
- Paving the way for more human-like AI responses, improving the practicality and safety of large language models
▲ (From left) Professor Jung-Woo Lee, and researchers Taehyun Cho, Seokhun Ju, and Seungyup Han, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University
Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that a research team led by Professor Jungwoo Lee in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering has developed a novel reinforcement learning technique applicable to large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT. Their paper proposing this technique was selected as a “Spotlight” paper—representing the top 2.6% of submissions—at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025), a leading academic venue in AI theory.
HodooAI, an AI automated learning platform founded by Professor Lee, presented the study titled “Policy-labeled Preference Learning: Is Preference Enough for RLHF” at ICML 2025, held in Vancouver, Canada, from July 13 to 20.
This achievement—being selected as a Spotlight paper at one of the world’s top AI conferences—demonstrates the international recognition of cutting-edge natural language processing AI expertise developed by SNU’s Cognitive Machine Learning Lab (CML) and HodooAI.
When large language models such as ChatGPT interact with users, they are trained to generate sentences aligned with human values—that is, coherent, high-quality responses that resemble human writing. This is achieved using a training method called Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). RLHF trains AI to “maximize a reward function” so that it prioritizes answers that humans prefer, serving as a core technology for AI alignment.
In recent years, RLHF has become a standard component of most language models to reduce bias and prevent the generation of illegal or harmful content. However, this approach has a critical limitation: due to its reward-function-centered, simplified learning structure, the model may be forced to compare two inferior sentences, introducing inefficiency into the training process and ultimately degrading model performance.
To address this limitation, Professor Lee’s team proposed a new reinforcement learning approach called Policy-labeled Preference Learning (PPL). Unlike conventional RLHF—which reflects user preference without considering the alignment quality of model outputs—PPL only incorporates preferences for outputs generated by well-trained, reliable AI models.
During the development of PPL, the team specifically targeted RLHF’s major weakness: the inefficient learning structure caused by comparing two low-quality, inferior sentences. Their solution considers the quality of AI model that produced each sentence and incorporates that information into the optimization process, enabling more precise and effective learning.
If widely adopted, this technology is expected to increase the success rate of alignment training for large language models by 100%, allowing everyday users to apply LLMs to practical tasks with greater confidence and safety. Academic researchers are also expected to leverage PPL to advance subsequent studies in AI alignment. Furthermore, this patented technology will serve as a core capability for generating “alignment-enhanced LLMs” on HodooAI’s AI platform.
Taehyun Cho, the first author and a researcher in SNU’s Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, remarked, “We expect this new technology to not only elevate Korea’s AI alignment capabilities to a world-class level but also improve the practicality and safety of large language models. Moving forward, I plan to focus on natural language processing research based on reinforcement learning.”
Professor Jungwoo Lee, who supervised the research, added, “I am delighted that our work was recognized among the top 2.6% of papers at ICML 2025, the most prestigious AI conference. We will continue to develop more innovative technologies that advance the technical capabilities of Korean AI research labs and AI startups.”
Professor Jungwoo Lee, regarded as one of Korea’s leading experts in Trustworthy AI, co-founded HodooAI with five graduate students from his lab. Co-authors Taehyun Cho, Seokhun Ju, and Seungyup Han—all researchers in SNU’s Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering—are currently dedicated to LLM and AI alignment research. They plan to pursue follow-up research in academia or join global corporate research labs in the future.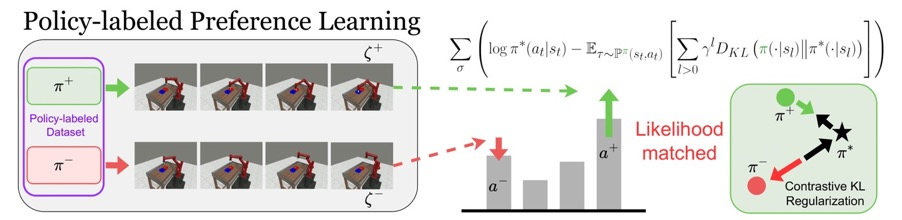
▲ Conceptual diagram of PPL addressing the limitations of traditional RLHF: Unlike previous methods that compare two dispreferred sentences meaninglessly, PPL considers the model level that generated each sentence to perform more precise optimization.
▲ Example application of the proposed PPL method in a robot simulation environment
[Reference Materials]
- Paper : “Policy-labeled Preference Learning: Is Preference Enough for RLHF”, International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025)
- Paper link : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.06273
[Contact Information]
Professor Jungwoo Lee, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University / +82-2-880-1754 / junglee@snu.ac.kr