- About
- Academics
-
Undergraduate Programs
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Architecture and Architectural Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy Resources Engineering
- Nuclear Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
-
Graduate Programs
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Architecture and Architectural Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy Systems Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Interdisciplinary Program in Technology, Management, Economics and Policy
- Interdisciplinary Program in Urban Design
- Interdisciplinary Program in Bioengineering
- Interdisciplinary Program in Artificial Intelligence
- Interdisciplinary Program in Intelligent Space and Aerospace Systems
- Chemical Convergence for Energy and Environment Major
- Multiscale Mechanics Design Major
- Hybrid Materials Major
- Double Major Program
- Open Programs
-
Undergraduate Programs
- Research
- Campus Life
- Communication
- Prospective Students
- International Office
News
Professor Young-Chang Joo of SNU College of Engineering Develops High-Performance Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction Catalyst
-
Uploaded by
관리자
-
Upload Date
2021.07.05
-
Views
868
Professor Young-Chang Joo of SNU College of Engineering Develops High-Performance Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction Catalyst
- Production of high value-added chemical raw materials with carbon dioxide,
a 'carbon neutral core technology'
- Published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' and recognized for its achievements

▲ (from left) Professor Young-Chang Joo of Seoul National University Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Dae-Hyun Nam of DGIST Department of Energy Science & Engineering, BK Professor Gun-Do Lee of Seoul National University Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Ph.D. student Ji-Yong Kim of Seoul National University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Seoul National University College of Engineering (Dean Kookheon Char) announced on June 18 that a research team led by Professor Young-Chang Joo of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a high-performance carbon dioxide electroreduction catalyst.
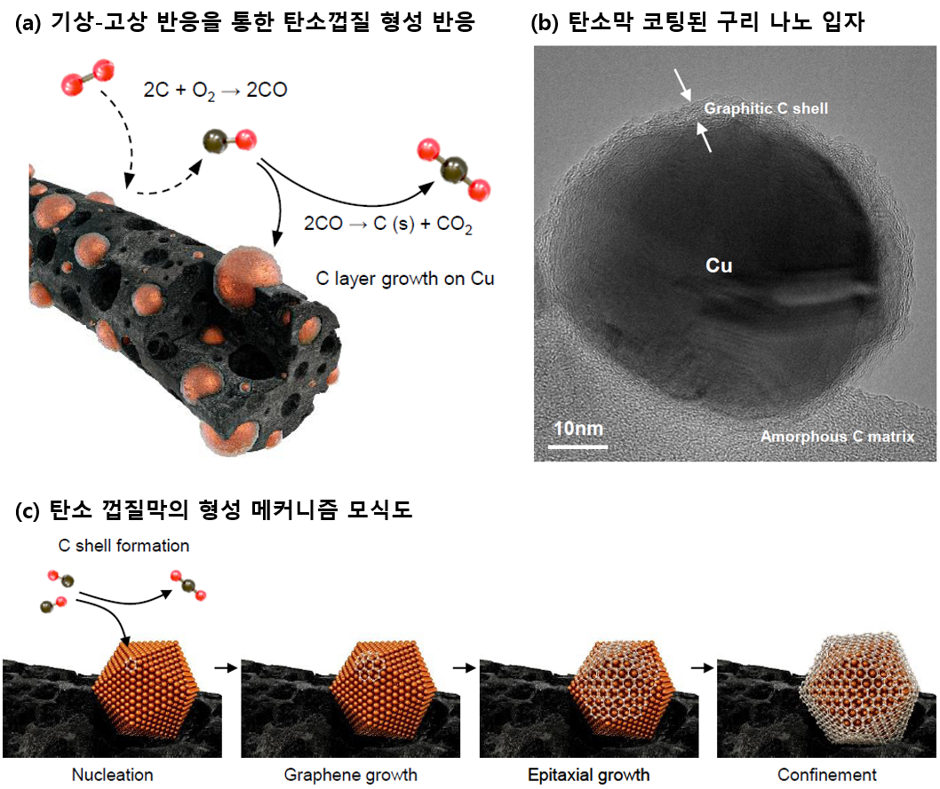
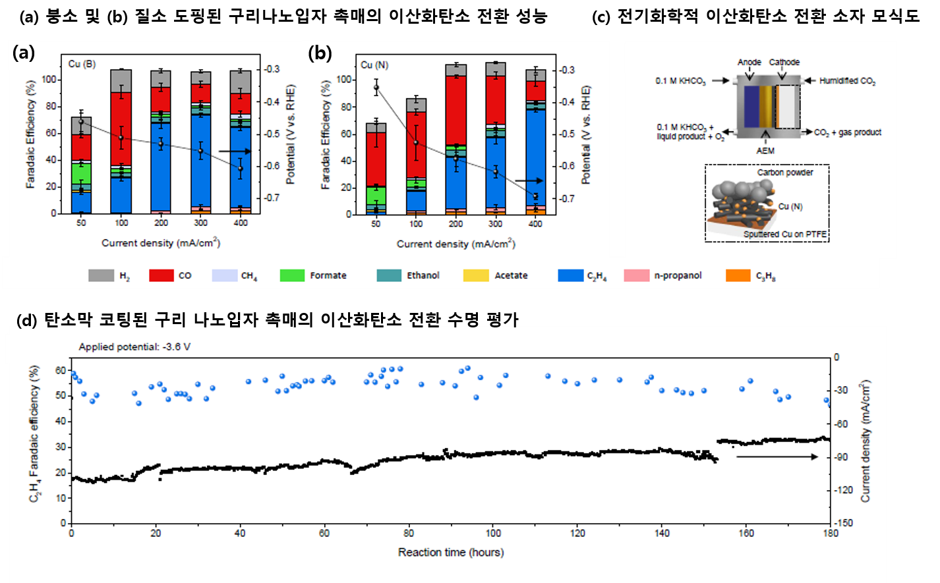
With the recent increase in environmental issues, the role of electrochemical catalysts in converting collected carbon dioxide into useful compounds such as ethylene using renewable energy is becoming highly important. Ethylene, called the 'rice' of the industrial field due to its high utilization value demonstrated by its use in plastic, rubber, various building materials and many others, has its existing production method involving the refining of oil, which produces large amounts of greenhouse gases. Although carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, can be converted directly to ethylene through electrochemical reactions using copper catalysts, existing copper catalysts have reported to not only have a 50% low ethylene selection, but also have the issue of having a very short life span in the reaction environment due to damage in its surface structures, requiring significant improvements in the dimension of both its utility and stability.
In response, a research team consisting of Professor Young-Chang Joo of the Seoul National University Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Dae-Hyun Nam of the DGIST Department of Energy Science & Engineering and BK Professor Gun-Do Lee of the Seoul National University Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed an electrochemical catalyst that not only achieves the highest level of efficiency but also dramatically improves stability by coating a thin carbon film on copper particles using the principle utilized in metal smelting.
The research team stated that they are hoping to take a step closer to commercializing technology that converts carbon dioxide into ethylene.
The research results, which were carried out with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Research Foundation's Future Material Discovery Project, were published on June 18 (Friday) in the international journal 'Nature Communications'.
<Attachment> (top) Diagram of the carbon film coating mechanism of a copper catalyst,
(bottom) Carbon dioxide conversion device performance